
On its own, CBD does not offer all the benefits of the hemp plant. When combined with terpenes, however, CBD unleashes its full potential. Terpenes enhance the effects of CBD that are already present, and they can also modify the effects of this cannabinoid to enhance some of its specific attributes.
In this guide, learn what terpenes are, and what their benefits are. While CBD is already well studied by the scientific community, terpenes are increasingly being researched and discovered for their application in humans.
1/ Introduction to terpenes
Terpenes are natural aromatic compounds found in cannabis and many other plants. Originally, they allow plants to perform primary functions, such as protection against high temperatures or against insects and predators.
They also allow, thanks to the aromatization, to facilitate the pollination of the plants by attracting the insects pollinators. Non-intoxicating yet offering impressive medicinal benefits, there are dozens of terpenes present in cannabis flowers.
Some of them, like limonene or pinene, may already be familiar to you. Limonene is the terpene that gives oranges a citrus smell, while pinene is the substance found in sap that produces the easily recognizable aroma of pine trees. Terpenes are ubiquitous in nature, but few plants besides cannabis bring together so many different terpenes in such a complex way.
Researchers have discovered more than 100 terpenes in cannabis flowers. For this article, we will stick to four common cannabis terpenes: beta-caryophyllene, limonene, linalool and pinene.
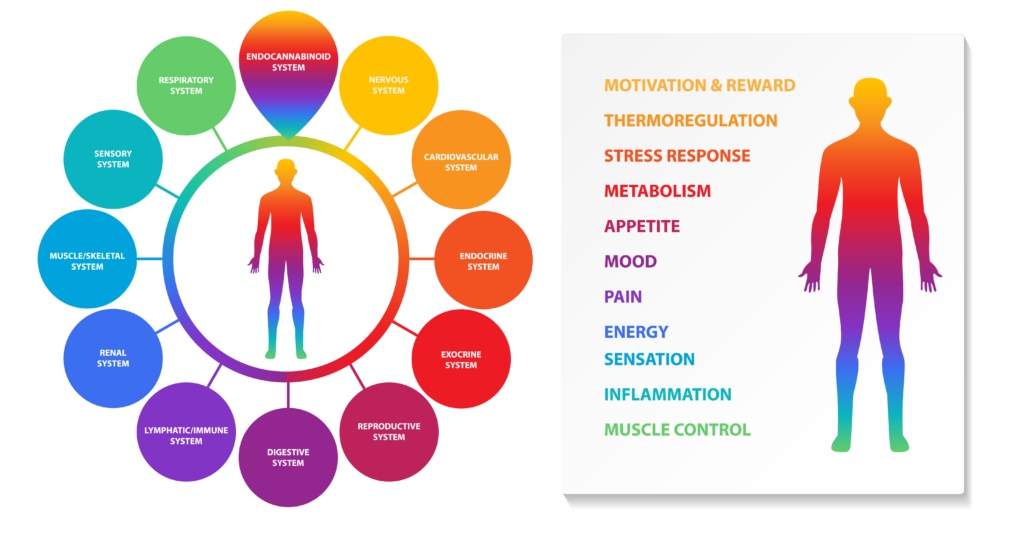
2/ The study of terpenes and their beneficial role on health
Many scientific discoveries have been made about each of these terpenes, and what you learn may surprise you:
The same terpene that makes red peppers spicy, beta-caryophyllene, is unique among terpenes because it acts as a cannabinoid in your body. Beta-caryophyllene won’t get you high, but it does activate your CB cannabinoid receptors, which transmit pain in the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
While research on beta-caryophyllene and pain has so far been limited to animals, early results from a recent study of the National Academy of Science entitled «Beta-caryophyllene is a dietary cannabinoid » indicate that this terpene should be heavily studied as a potential pain treatment.
Limonene, a citrus terpene found, for example, in lemons, has been the subject of intensive research for its potential anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Many common medical conditions have already been linked to oxidative stress and inflammation, and it is possible that the extent of damage caused by these two bodily phenomena is far greater than we currently know.
The study published on the Journal of Food Science « Anti-inflammatory Effects of Limonene from Yuzu Citrus » carried out on animals and whose purpose was to study inflammation-related effects, provided evidence that limonene may have anti-inflammatory properties in vitro. A third study in human cell cultures indicated that limonene may reduce oxidative stress in the context of leukemia.
The third widely researched terpene, linalool, is the terpene that makes lavender smell so soothing. Scientists have studied in « Antidepressant activity of Litsea glaucescens essential oil: Identification of β-pinene and linalool as active principles », published on the Journal of Ethnopharmacology, the potential usefulness of this relaxing terpene for various conditions. Most notable, however, is the research on linalool for depression and anxiety. For example, one study showed that linalool could reduce symptoms related to anxiety and depression in animals undergoing various stress tests.
Finally, pinene has been studied, in the same study as mentioned before, for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. However, what makes pinene unique is the research on this terpene as a potential bronchodilator.
Korean researchers have provided evidence that pinene may be useful as a bronchodilator in the context of allergic attacks in mice. As a bronchodilator is a substance that opens the airways and helps breathing, pinene could be very useful in the future treatment of respiratory diseases.
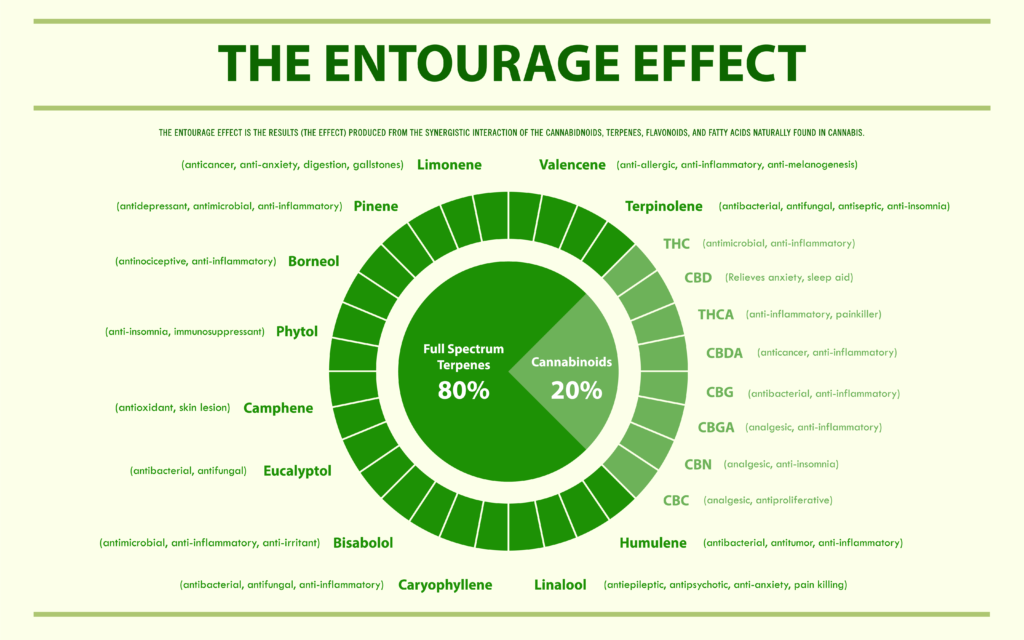
3/ The entourage effect, a synergistic mechanism enhancing the effect of cannabinoids
Another mechanism called “entourage effect” is also the subject of much interest by the scientific community.
While all the mechanisms behind this phenomenon have not been discovered, there is considerable evidence that certain terpenes can improve the body’s handling of CBD and other cannabinoids through a type of synergy: the so-called entourage effect.
Without the terpenes, CBD is not able to transmit all the benefits of its molecule. Each terpene enhances the benefits of CBD in a different way, but together, a complete terpene profile of the cannabis flower allows CBD to reach its maximum effectiveness.
People who smoke or vape cannabis flower (whether CBD or THC) have long reported that different strains provide different effects. Some researchers have speculated that the entourage effect may be behind these enhanced and stimulated effects, so adding terpenes to CBD flowers or within CBD extracts offers all the extra benefits that terpenes provide.
Manufacturers of CBD products, such as CBD oil or CBD extracts, often do not include terpenes in their products and often omit terpene analysis in their tests. The addition of terpenes in these products can however deeply modify its effects.
Everyone knows the saying: alone we go faster, together we go further. It is the same for CBD: isolated from its surroundings, it cannot deliver its benefits in an optimal way. Reunited with the terpenes that it gave birth to in the cannabis flower, CBD can however do much more.
At Lilium Xtract, we are passionate about the cannabis plant, experts in terpene extractions and cannabis fragrance & aromas reproduction. You can find in our online store the best terpenes on the market to give a powerful smell to your flowers or CBD extractions, or a cannabis taste to E-liquids, foods or drinks.
Don’t take our word for it and try them for free! Receive your sample pack by clicking here :
Sources of information :
· Gertsch, J., Leonti, M., Raduner, S., Racz, I., Chen, J. Z., Xie, X. Q., Altmann, K. H., Karsak, M., & Zimmer, A. . Beta-caryophyllene is a dietary cannabinoid. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
· LaVigne, J. E., Hecksel, R., Keresztes, A., & Streicher, J. M. . Cannabis sativa terpenes are cannabimimetic and selectively enhance cannabinoid activity. Scientific Reports
· Hirota, R., Roger, N. N., Nakamura, H., Song, H. S., Sawamura, M., & Suganuma, N. . Anti-inflammatory Effects of Limonene from Yuzu Citrus junos Tanaka Essential Oil on Eosinophils. Journal of Food Science, , H–H.
· Yu, L., Yan, J., & Sun, Z. . D-limonene exhibits anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties in an ulcerative colitis rat model via regulation of iNOS, COX-, PGE and ERK signaling pathways. Molecular Medicine Reports
· Guzmán-Gutiérrez, S., Gómez-Cansino, R., García-Zebadúa, J., Jiménez-Pérez, N., & Reyes-Chilpa, R. . Antidepressant activity of Litsea glaucescens essential oil: Identification of β-pinene and linalool as active principles. Journal of Ethnopharmacology
· Nam, S. Y., Chung, C. K., Seo, J. H., Rah, S. Y., Kim, H. M., & Jeong, H. J. . The therapeutic efficacy of α-pinene in an experimental mouse model of allergic rhinitis. International Immunopharmacology
·J. K. & Bohlmann | Terpenes in Cannabis sativa – From plant genome to humans. Plant Science

